Raging Forest Fires Grip the Nation: Experts Warn of Worsening Situation Amid Lack of Rain
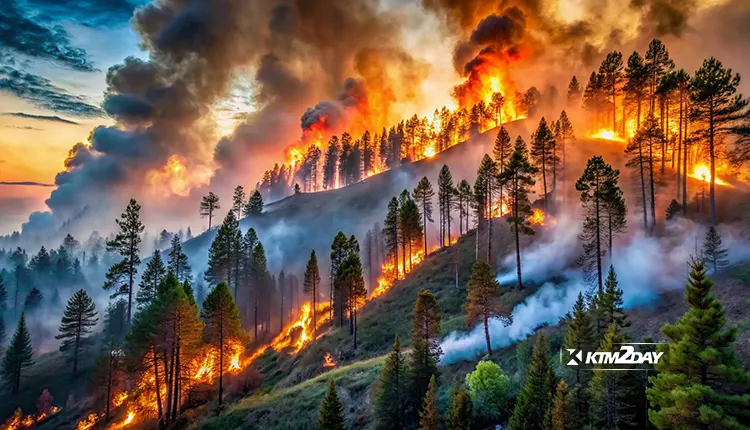


Kathmandu – The situation of forest fires across the country is rapidly deteriorating, with the National Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Authority reporting that fires are raging in 165 places in 39 districts as of today.
Stakeholders have expressed grave concerns that without timely rainfall, the forest fires will continue to spread and intensify. However, the Water and Weather Forecasting Division under the Department of Water and Meteorology has stated that there is no immediate prospect of the kind of rain that would control the fires.
“For the next three days, there is a possibility of scattered rains with partial showers in some hilly areas of Koshi, Gandaki, Karnali,” said Meteorologist Govind Jha, “but there is no immediate possibility of the type of rain that will control forest fires.” In other parts of the country, the weather is expected to remain clear.
Tragic Loss of Life and Widespread Destruction
The raging forest fires have already claimed two lives in Lalitpur, with Shankar Pahari and Ramesh Pahari losing their lives while attempting to extinguish the blaze in the Tapeshwar Community Forest.
Sundar Sharma, a forest fire expert at the National Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Authority, has expressed deep concern over the situation. “Due to Nepal’s geographical situation, more problems are arising in control,” he said, “It has not rained, but the fire is spreading due to the wind blowing the fire.”
According to Sharma, the districts of Salyan, Surkhet, Kailali, Dailekh, and Doti have been particularly affected by the fires. He also revealed that 80 houses are burned down every year due to forest fires in Nepal.
Lack of Sustainable Forest Management Exacerbates the Crisis
Forest expert Dr. Soni Baral Gowli has attributed the increasing incidence of forest fires to the lack of sustainable forest management, emphasizing the need for a shift from conservation-oriented to management-oriented forest development.
Theer Prasad Koirala, a Forest Officer at the Division Forest Office in Lalitpur, has also highlighted the role of human activities, such as lighting cigarettes and throwing cigarette butts in the forest, as well as the practice of setting fires to drive away wild animals, as contributing factors to the escalating crisis.

Efforts to Curb the Fires: Challenges and Strategies
In response to the situation, the Division Forest Offices have initiated widespread public awareness campaigns and have started installing CCTV cameras in some areas to monitor and deter human-caused fires.
The Forest Act 2076 also provides for punishments of up to three years of imprisonment or a fine of up to 60,000 rupees, or both, for those found guilty of starting fires in national forests.
Furthermore, the Forest Fire Management Strategy 2067 aims to build and strengthen the policy and institutional structures necessary to manage fires, mobilize local communities, civil society, government, and non-government agencies for fire prevention and control, and prepare for advance information on the risks that may arise from fires.
However, Thakur Bhandari, President of the Community Forest Users Federation (Fecofan), has expressed concerns about the lack of effective implementation of the existing strategies. “Consumers have lost their lives while trying to control the fire in the forest,” he said.
As the nation grapples with the escalating forest fire crisis, urgent and coordinated action is needed to address the underlying issues, strengthen fire management strategies, and protect lives, livelihoods, and the precious natural resources that are at risk.